Creating GUIs with LVGL (V7)
In this tutorial you will learn to use LVGL (Light and Versatile Graphics Library) to create a simple graphical user interface that consists of a label which updates itself.
Overview
In this tutorial you will learn to use LVGL to create a simple graphical user interface that consists of a text label which updates itself.
Goals
- Understanding the structure to build LVGL interfaces.
- Building a simple UI with a text label.
- Configuring the setup to display the User-Interface.
Required Hardware and Software
- Portenta H7 (ABX00042)
- USB-C® cable (either USB-A to USB-C® or USB-C® to USB-C®)
- Arduino IDE 1.8.10+ or Arduino Pro IDE 0.0.4+
- USB-C® hub with HDMI
- External monitor
- HDMI cable
The Light and Versatile Graphics Library
Graphical User interfaces are needed for visualizing information and interacting with certain aspects of an application. The Light and Versatile Graphics Library, also known as LVGL, is an open-sourced library used to create graphical user-interfaces for microcontrollers and high-end processors. The light weight embedded library provides all the necessary widgets and user interface elements that will allow you to easily create user interfaces for displays and touch screens.
Instructions
Building a Simple GUI
This tutorial will guide you through building a basic user interface using the LVGL Library, which you can download using the Arduino Library Manager. The setup for this tutorial requires you to first upload the finished sketch file to the Portenta board. You will then connect the board to a USB-hub in order to connect it to an external monitor as well. Once the hub is powered externally, a graphical user interface with a label will be displayed on the screen.
1. The Basic Setup
Begin by plugging your Portenta board into the computer using a USB-C® cable and open the Arduino IDE. If this is your first time running Arduino sketch files on the board, we suggest you check out how to set up the Portenta H7 for Arduino before you proceed.
2. Download the LVGL Library
Next, select 'Portenta' in the Tools > Board menu before installing lvgl from the Library Manager. Then go to Sketch > Include Libraries > Manage Libraries and search for LVGL. Download lvgl by kisvegabor.
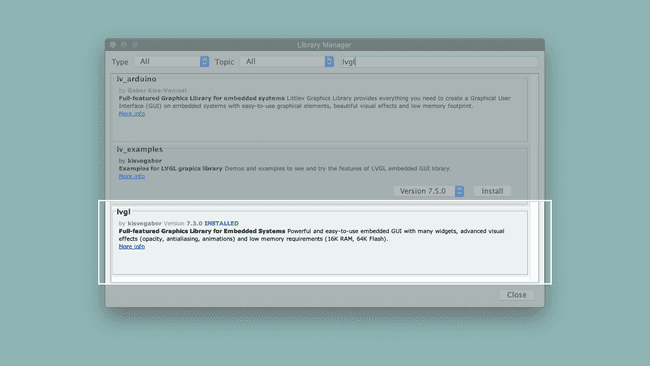
The sketches that we show are using the version 7.11.0. If you have the version 8 or greater you will need to make changes on the code, check LVGL API docs to see the update changes: https://docs.lvgl.io/master/.
3. Adding a Label Widget
Let's start by including the library that we are going to use.
1#include "Portenta_LittleVGL.h"Create a custom label widget named
label1static lv_obj_t *label;Then inside the
setup()1void setup() {2 Serial.begin(9600);3
4 // Initialize Portenta's video interface5 portenta_init_video();6
7 // Setting up the label making it a child of the screen8 label = lv_label_create(lv_scr_act(), NULL);9
10 // Set the label's text11 lv_label_set_text(label , "Counter");12
13 // We move it to the center of the screen and align it centered14 lv_obj_align(label, NULL, LV_ALIGN_CENTER, 0, 0);15}This sketch creates a label that will be displayed in the center of the connected monitor.
4. Connect an External Monitor
Compile and upload the sketch to your Portenta H7. At this point your board becomes the host. Unplug the board from your computer and connect it to the USB-hub along with a monitor, which is connected to the HDMI port. Power up your hub by connecting it to an external power source and the monitor will display a label saying
CounterIf you are not familiar how the USB host works, we recommend you to have a look at the USB Host tutorial.
Our label object currently has LVGL's default style. If you want to customize the style, you can have a look at LVGL's documentation.
5. Creating a Simple Counter
Let's create a counter that increases each second and update the label on the screen. To do so, you have to create a label and an updating task that is going to update the label periodically and change its value. This is possible using an LVGL concept called 'Task'.
First, you can create a counter variable at the beginning of the program (before the
setup()1int counter = 0;Then, you can create the function that is going to update the value of the counter and its label. Add it to the sketch just before the
setup()1static void updateCounterTask(lv_task_t *task) {2 // Print the count to the Serial monitor3 Serial.println(counter);4
5 // Update the text of the label6 lv_label_set_text_fmt(label, "%d" , counter);7
8 // Increase the count number9 counter++;10}As the last line inside the
setup()updateCounterTask()1// Create a task to update the counter2lv_task_create(updateCounterTask, 1000, LV_TASK_PRIO_MID, NULL);Finally, in the loop function add
lv_task_handler()1void loop() {2 // put your main code here, to run repeatedly:3 lv_task_handler();4}6. Upload the Sketch
Below is the complete sketch of the tutorial that updates the label's text with an incrementing counter value. Upload the sketch to your Portenta H7 and connect it to an external monitor as described in Step 4.
1#include "Portenta_LittleVGL.h"2
3static lv_obj_t *label;4int counter = 0;5
6static void updateCounterTask(lv_task_t *task) {7 // Print the count to the Serial monitor8 Serial.println(counter);9
10 // Update the text of the label11 lv_label_set_text_fmt(label, "%d" , counter);12
13 // Increase the count number14 counter++;15}16
17void setup() {18 Serial.begin(9600);19
20 // Initialize Portenta's video interface21 portenta_init_video();22
23 // Setting up the label making it a child of the screen24 label = lv_label_create(lv_scr_act(), NULL);25
26 // Set the label's text27 lv_label_set_text(label , "Counter");28
29 // We move it to the center of the screen and align it centered30 lv_obj_align(label, NULL, LV_ALIGN_CENTER, 0, 0);31
32 // Create a task to update the counter33 lv_task_create(updateCounterTask, 1000, LV_TASK_PRIO_MID, NULL);34}35
36void loop() {37 // put your main code here, to run repeatedly:38 lv_task_handler();39}Conclusion
This tutorial shows how to build a simple user interface with your Portenta. Starting with a static view in the monitor and then converting it into a simple dynamic application that features an updating variable on the screen. The tutorial also shows how to use the "task" feature of LVGL to run instructions recurrently.
Next Steps
Now that you know how to build a simple UI for a screen, you can try to add more labels to the screen to show various information or try out different LVGL widgets.
Troubleshooting
Counter Label Does Not Update
- Make sure that the label and task are declared on top of the sketch, outside the
andsetup()
like a normal variable.loop() - Check if the task has the same structure in the first declaration and the function creation.
- Look inside the
and see ifloop()
is there.lv_task_handler()
Sketch Upload Troubleshooting
- If you have troubles uploading the sketch, try to first set the board in bootloader mode, by clicking the reset button twice. Then you should see the built-in LED pulsating.
- If you uploaded the sketch and you do not have any output in the display, make sure you have
in theportenta_init_video()
.setup() - Unplug and plug the HDMI cable in again.
- Reset the Portenta once it is connected to the USB-hub.
Suggest changes
The content on docs.arduino.cc is facilitated through a public GitHub repository. If you see anything wrong, you can edit this page here.
License
The Arduino documentation is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 license.